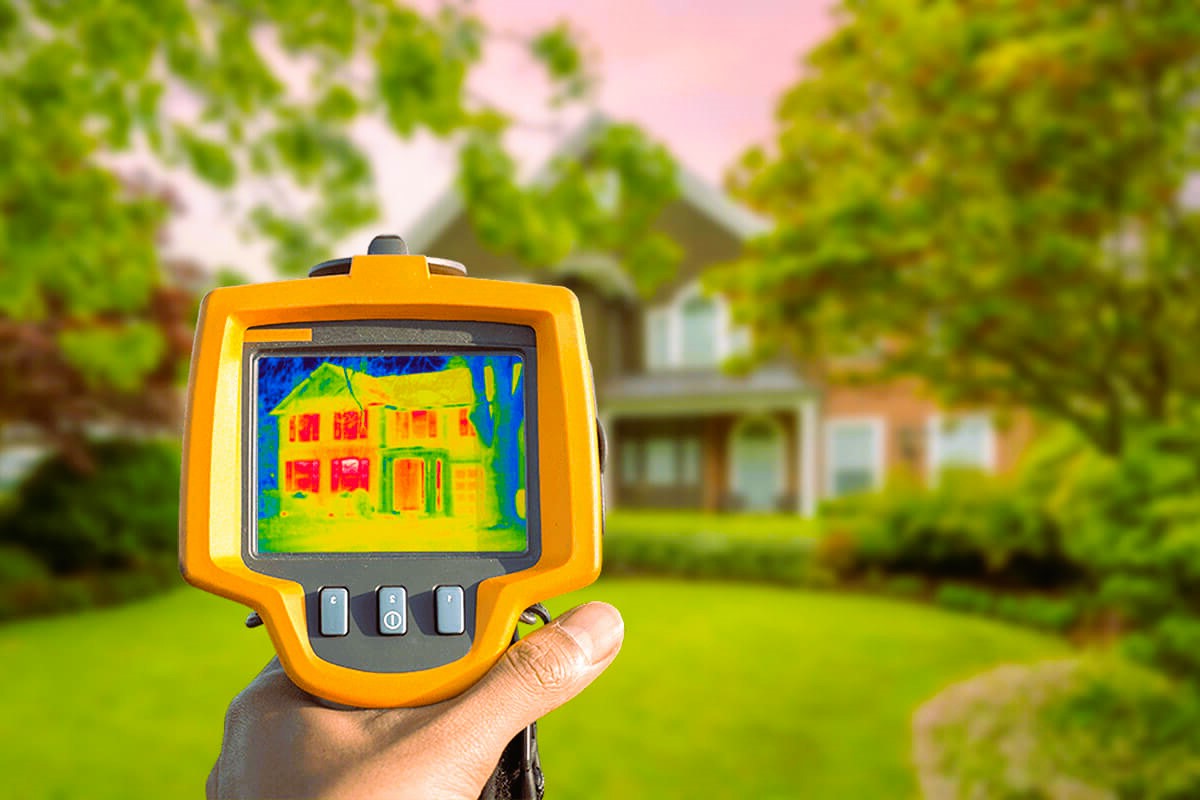
Window glazing plays a crucial role in the performance and energy efficiency of windows. It refers to the process of adding an extra layer of material to the window glass to enhance its thermal insulation properties, reduce noise transmission, and improve overall comfort. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different window glazing options available, their benefits, and considerations when selecting the right glazing for your windows.
- Single Glazing:
Single glazing refers to windows that have only one layer of glass without any additional glazing materials. While single glazing is the most basic and affordable option, it offers minimal insulation properties and lacks efficiency in thermal performance. It allows heat to easily transfer through the glass, leading to heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer. Single glazing is commonly found in older or historic homes, but it is not recommended for energy-efficient purposes.

- Double Glazing:
Double glazing involves the use of two layers of glass separated by a layer of air or gas, typically argon or krypton, in the sealed space between them. This creates an insulating barrier that significantly reduces heat transfer and improves energy efficiency. Double glazing helps maintain a comfortable indoor temperature, reduces energy consumption for heating and cooling, and minimizes condensation on the glass. It also provides better sound insulation compared to single glazing. Double glazing is a popular and cost-effective choice for homeowners looking to improve energy efficiency and comfort. Like the article? Read more about window balancers.
- Triple Glazing:
Triple glazing takes the concept of double glazing a step further by adding a third layer of glass, creating two insulating air or gas-filled spaces. Triple glazing offers superior thermal performance and sound insulation compared to both single and double glazing. It provides excellent energy efficiency by further reducing heat transfer and improving overall comfort. However, it is important to note that the additional glass and gas layers make triple glazing heavier and more expensive than double glazing. It is commonly used in colder climates or in areas where noise reduction is a high priority.
- Low-E Coating:
Low-emissivity (Low-E) coating is a thin, virtually invisible layer of metallic particles applied to the surface of the glass. This coating helps control the amount of heat and light that passes through the window. Low-E coating is designed to reflect infrared heat back into the room while allowing visible light to pass through, resulting in improved energy efficiency and reduced solar heat gain. It also helps prevent UV rays from entering the interior, protecting furnishings and fabrics from fading. Low-E coating can be applied to both single and double glazing, enhancing their performance.
- Gas Filling:
Gas filling is an option commonly used in double and triple glazing to further enhance the thermal insulation properties. The space between the glass layers is filled with an inert gas, such as argon or krypton. These gases have a higher density than air, reducing heat transfer and improving insulation. Gas filling helps to enhance the overall energy efficiency and performance of the window, particularly in reducing heat loss. Argon gas is the most commonly used due to its cost-effectiveness and availability.

- Considerations for Choosing Window Glazing:
- Climate: Consider the climate in your region when choosing window glazing. For colder climates, triple glazing or double glazing with Low-E coating and gas filling may be more beneficial in reducing heat loss. In warmer climates, double glazing with Low-E coating can help reduce heat gain.
- Energy Efficiency: Look for windows with a high energy efficiency rating, such as those certified by organizations like ENERGY STAR. These windows have been tested and meet specific performance criteria for energy efficiency.
- Noise Reduction: If noise reduction is a priority, consider double or triple glazing with a thicker glass and gas filling, as they provide better sound insulation.
- Budget: Determine your budget and balance it with the desired energy efficiency and performance. Triple glazing and advanced glazing options may come at a higher cost compared to double glazing or single glazing.
- Aesthetics: Consider the appearance and visual clarity of the glazing options. Some glazing options may have a slight tint or reflectivity, which can impact the overall aesthetics of the window.
- Maintenance: Consider the maintenance requirements of the different glazing options. Some coatings may require special care or cleaning techniques.
In conclusion, selecting the right window glazing option is crucial for energy efficiency, comfort, and overall performance. Double glazing is a popular and cost-effective choice, providing significant improvements in insulation and sound reduction. Triple glazing offers even higher thermal performance and sound insulation, ideal for colder climates. Low-E coating and gas filling further enhance the energy efficiency of the windows. Consider your climate, budget, and desired performance to make an informed decision when choosing window glazing options for your home.